PART A: MATLAB practice.
1. Open MATLAB. Open the editor and copy paste the following code. Name your code as FirstCode.m
Save the resulting plot as a JPEG image and put it here.
 |
| Figure 1: Graph of code given |
2. What does clear all do?
The clear all command clears the command terminal.
3. What does close all do?
The close all command clears the workspace of all figures and the command terminal for a brand new workspace.
4. In the command line, type x and press enter. This is a matrix. How many rows and columns are there in the matrix?
1 row, 5 columns.
5. Why is there a semicolon at the end of the line of x and y?
The semicolon is used to end a command.
6. Remove the dot on the y = 2.^x; line and execute the code again. What does the error message mean?
The error code means that in order to use the power (^) function, the object being taken to a power must be of a scalar value. The dot is used to signify a number as a scalar.
7. How does the LineWidth affect the plot? Explain.
Line width affects the plot
8. Type help plot on the command line and study the options for plot command. Provide how you would change the line for plot command to obtain the following figure (Hint: Like ‘LineWidth’, there is another property called ‘MarkerSize’)
 |
| Example graph to replicate. |
 |
| Our graph |
plot(x, y, '-ro', 'LineWidth', 6, 'MarkerSize', 20);
10. Provide the code for the following figure. You need to figure out the function for y. Notice there are grids on the plot.
>> clear all;
close all;
x = [1 2 3 4 5];
y = 2.^x;
plot(x, y,':ks', 'LineWidth', 6, 'MarkerSize', 18);
grid
xlabel('Numbers', 'FontSize', 12)
ylabel('Results', 'FontSize', 12)
 |
| Picture of graph represented by code above |
11. Degree vs. radian in MATLAB:
a. Calculate sinus of 30 degrees using a calculator or internet.
Sin(30 Degrees) = .5
b. Type sin(30) in the command line of the MATLAB. Why is this number different? (Hint: MATLAB treats angles as radians).
Sin(30) = -0.9880 This is the value when calculations are being done in radians rather than degrees.
c. How can you modify sin(30) so we get the correct number?
by typing sind(30), this makes the function calculate in degrees rather than radians.
12. Plot y = 10 sin (100 t) using Matlab with two different resolutions on the same plot: 10 points per period and 1000 points per period. The plot needs to show only two periods. Commands you might need to use are linspace, plot, hold on, legend, xlabel, and ylabel. Provide your code and resulting figure. The output figure should look like the following:
>> clear all;
close all;
t = linspace(0,0.126,10);
y = 10*(sin(100*t));
x = linspace(0,0.126,1000);
z = 10*(sin(100*x));
plot(t, y, '-ro',x, z, 'k' )
axis([0 .14 -10 10]);
xlabel('Time(S)')
ylabel('y function');
legend('Coarse', 'Fine');
 |
| Example |
 |
| Our version |
13. Explain what is changed in the following plot comparing to the previous one.
Every value of Z that was found to be greater than 5 was changed to 5.
14. The command find was used to create this code. Study the use of find (help find) and try to replicate the plot above. Provide your code.
>> clear all;
close all;
t = linspace(0,0.126,10);
y = 10*(sin(100*t));
x = linspace(0,0.126,1000);
z = 10*(sin(100*x));
f = find(z>5);
z(f) = 5;
plot(t, y, '-ro',x, z, 'k' )
axis([0 .14 -10 10]);
xlabel('Time(S)')
ylabel('y function');
legend('Coarse', 'Fine');
 |
| Our graph using find function |
PART B: Filters and MATLAB
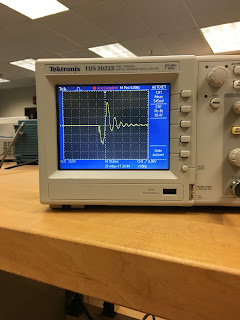
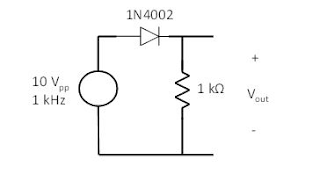
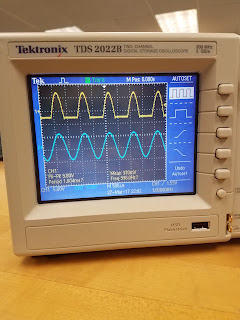
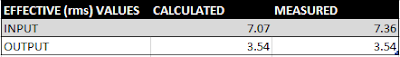
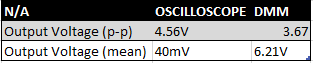
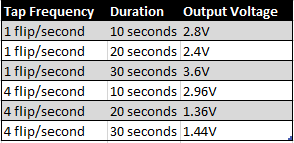
1. Build a low pass filter using a resistor and capacitor in which the cut off frequency is 1 kHz. Observe the output signal using the oscilloscope. Collect several data points particularly around the cut off frequency. Provide your data in a table.
 |
| Low pass filter table |
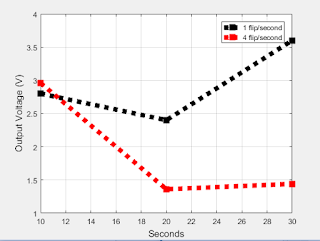
2. Plot your data using MATLAB. Make sure to use proper labels for the plot and make your plot line and fonts readable. Provide your code and the plot.
 |
| Low pass filter graph |
>> clear all;
close all;
x = [0 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4];
y = [3.7 3.68 3.6 3.5 3.38 3.26 3.12 2.98 2.85 2.85 2.72 2.6 2.47 2.37 2.26];
plot(x, y)
xlabel('Frequency(KHz)', 'FontSize', 12)
ylabel('Vout(rms)', 'FontSize', 12)
>>
3. Calculate the cut off frequency using MATLAB. find command will be used. Provide your code.
Cutoff frequency between 1.1 and 1.4 Khz
clear all;
close all;
x = [0 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4];
y = [0 3.7 3.68 3.6 3.5 3.38 3.26 3.12 2.98 2.85 2.72 2.6 2.47 2.37 2.26];
z = [0 1.05 1.04 1.02 .99 .96 .92 .88 .84 .81 .77 .74 .69 .67 .64];
plot(x, z, )
s = find(z == 0.70)
x(s)
4. Put a horizontal dashed line on the previous plot that passes through the cutoff frequency.
 |
| Low pass filter graph with cut off frequency shown |
clear all;
close all;
x = [0 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4];
y = [3.7 3.68 3.6 3.5 3.38 3.26 3.12 2.98 2.85 2.85 2.72 2.6 2.47 2.37 2.26];
z = [0 1.05 1.04 1.02 .99 .96 .92 .88 .84 .81 .77 .74 .69 .67 .64];
plot(x, z)
xlabel('Frequency(KHz)', 'FontSize', 12)
ylabel('Vout(rms)', 'FontSize', 12)
hold on;
x = [0 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4];
z = .707
plot(x,z,'k+', 'LineWidth', 6)
xlabel('Frequency (kHz)', 'Fontsize', 12)
ylabel('Vout/Vin (V)', 'FontSize', 12)
hold off;
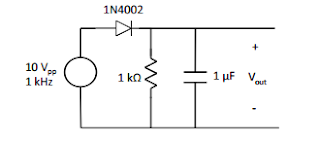
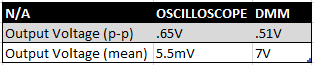
High Pass Filter (1-4)
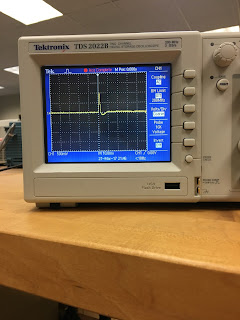
1.
 |
| High pass filter table |
clear all;
close all;
x = [0 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4];
y = [0 .5 .7 1.05 1.35 1.63 1.86 1.97 2.03 2.11 2.14 2.16 2.17 2.17 2.18];
z = [0 .14 .19 .29 .37 .46 .52 .55 .57 .59 .6 .61 .61 .61 .62];
plot(x, z)
xlabel('Frequency(KHz)', 'FontSize', 12)
ylabel('Vout(rms)', 'FontSize', 12)
hold on;
x = [0 .1 .2 .3 .4 .5 .6 .7 .8 .9 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4];
z = .4
plot(x,z,'k+', 'LineWidth', 6)
xlabel('Frequency (kHz)', 'Fontsize', 12)
ylabel('Vout/Vin (V)', 'FontSize', 12)
hold off;
 |
| High pass filter graph with cutoff frequency shown |